The key differences between RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10 lie in their data storage methods, fault tolerance, performance, and required number of disks:
| RAID Level | Storage Method | Minimum Disks | Fault Tolerance | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 1 | Mirroring (exact copy on two or more disks) | 2 | Can tolerate failure of 1 disk | High data redundancy, simple recovery, improved read speed | Storage capacity is 50% of total disk space; no striping |
| RAID 5 | Block-level striping with distributed parity | 3 | Can tolerate failure of 1 disk | Good balance of storage efficiency, fault tolerance, and read performance | Slower write speeds due to parity calculations |
| RAID 6 | Block-level striping with dual distributed parity | 4 | Can tolerate failure of 2 disks | Higher fault tolerance than RAID 5 | Even slower write speeds than RAID 5 due to double parity |
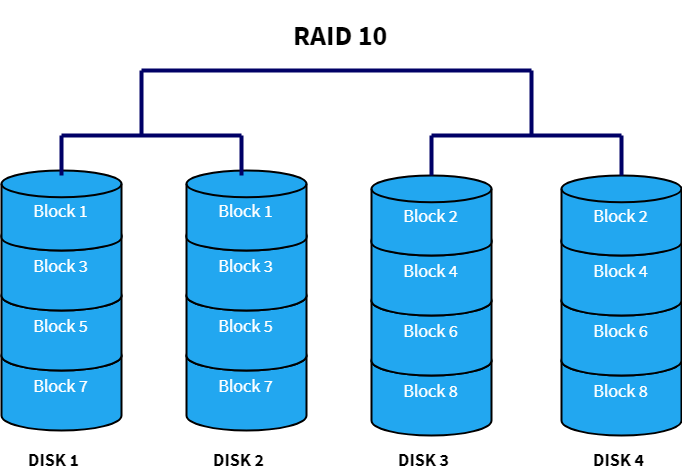
| RAID 10 (RAID 1+0) | Combination of striping and mirroring | 4 | Can tolerate failure of one disk per mirrored pair | High performance and fault tolerance, faster than RAID 5/6 | Requires more disks, storage capacity is 50% of total disk space |
Detailed Explanation:
-
RAID 1 duplicates data exactly on two or more disks (mirroring). If one disk fails, the data is still available on the other disk(s). It offers improved read performance but write speed is similar to a single disk. However, usable storage is only half of the total disk capacity because data is fully duplicated.
-
RAID 5 stripes data across all disks with distributed parity information. It requires at least three disks and can tolerate the failure of one disk without data loss. It provides better storage efficiency than RAID 1 because parity uses less space than full mirroring. Write speeds are slower due to parity calculations, but read speeds are good.
-
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5 but uses two parity blocks distributed across disks, allowing it to tolerate failure of two disks simultaneously. This increases data protection but further reduces write performance due to extra parity overhead. It requires at least four disks.
-
RAID 10 combines RAID 1 and RAID 0 by striping data across mirrored pairs. It requires a minimum of four disks. This setup offers the speed benefits of striping and the redundancy of mirroring. It can tolerate multiple disk failures as long as they are not in the same mirrored pair. Storage capacity is half of the total disk space due to mirroring.
In summary, RAID 1 is best for simple mirroring and reliability, RAID 5 balances capacity and fault tolerance with moderate performance, RAID 6 offers higher fault tolerance at the cost of write speed, and RAID 10 provides high performance and fault tolerance but requires more disks and sacrifices storage capacity.


















Ang PH Ranking ay nag-aalok ng pinakamataas na kalidad ng mga serbisyo sa website traffic sa Pilipinas. Nagbibigay kami ng iba’t ibang uri ng serbisyo sa trapiko para sa aming mga kliyente, kabilang ang website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, at TikTok traffic. Ang aming website ay may 100% kasiyahan ng customer, kaya maaari kang bumili ng malaking dami ng SEO traffic online nang may kumpiyansa. Sa halagang 720 PHP bawat buwan, maaari mong agad pataasin ang trapiko sa website, pagandahin ang SEO performance, at pataasin ang iyong mga benta!
Nahihirapan bang pumili ng traffic package? Makipag-ugnayan sa amin, at tutulungan ka ng aming staff.
Libreng Konsultasyon