RAID storage efficiency and drive requirements depend on the RAID level chosen, balancing capacity, performance, and fault tolerance.
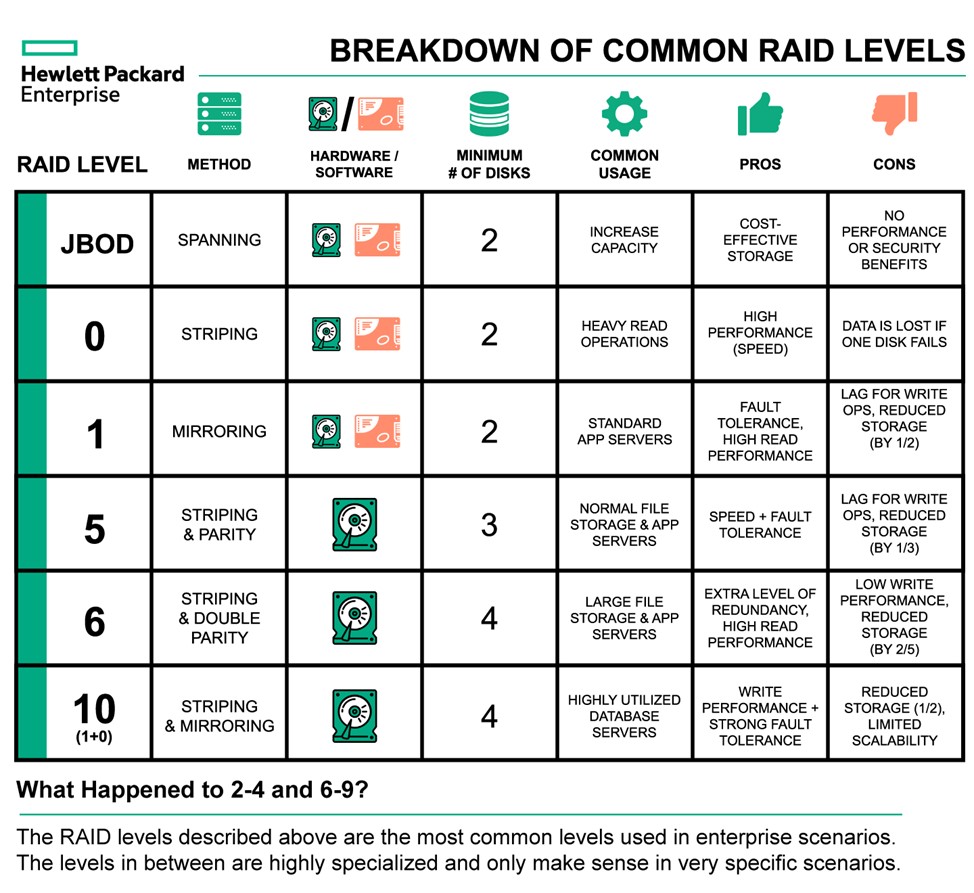
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) combines multiple drives into one logical unit to improve speed, increase capacity, and provide data redundancy. The efficiency and number of drives required vary by RAID configuration:
-
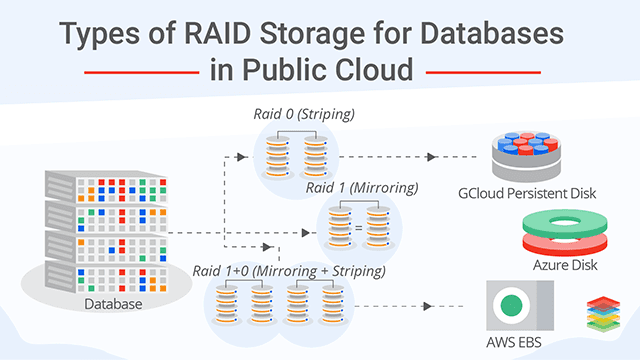
RAID 0 (Striping): Uses at least 2 drives, combining their capacity fully for maximum speed but offers no redundancy. Storage efficiency is 100% (all drive space usable), but if one drive fails, all data is lost.
-
RAID 1 (Mirroring): Requires at least 2 drives, storing identical copies on each. Storage efficiency is about 50% because half the total drive space is used for redundancy. It provides excellent fault tolerance.
-
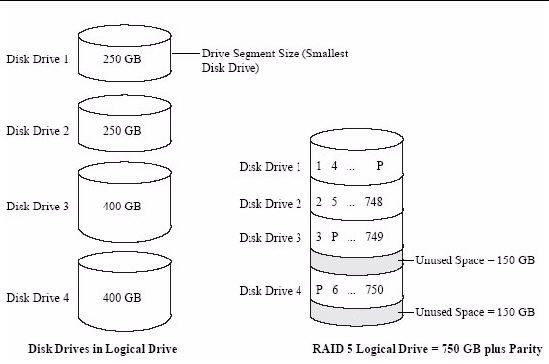
RAID 5 (Striping with parity): Needs at least 3 drives. It stripes data and parity information across drives, allowing one drive to fail without data loss. Storage efficiency is roughly ((N-1)/N), where (N) is the number of drives (e.g., with 4 drives, 75% efficiency). It balances capacity, performance, and fault tolerance.
-
RAID 6 (Double parity): Requires at least 4 drives and can tolerate two drive failures. Storage efficiency is ((N-2)/N), lower than RAID 5 but with higher fault tolerance.
-
Nested RAID levels (e.g., RAID 10): Combine mirroring and striping, requiring at least 4 drives. Storage efficiency is about 50%, but with improved performance and fault tolerance.
Key points about RAID storage efficiency and drive requirements:
-
Using identical drives (same make, model, and capacity) is recommended for best performance and reliability.
-
RAID increases storage capacity by combining multiple drives but some capacity is used for redundancy depending on the RAID level.
-
Fault tolerance varies: RAID 1, 5, and 6 provide redundancy to protect against drive failure, but RAID 0 does not.
-
RAID improves read/write speeds by parallelizing data operations across drives, enhancing performance especially in RAID 0, 5, and 10.
-
The number of drives affects storage efficiency: more drives in RAID 5 or 6 increase usable capacity but also increase rebuild times if a drive fails.
-
RAID is not a substitute for backups; regular backups are still necessary.
In summary, RAID storage efficiency depends on the RAID level and number of drives, with trade-offs between usable capacity, performance, and fault tolerance. The minimum number of drives ranges from 2 (RAID 0, 1) to 4 or more for advanced levels. Using identical drives and monitoring their health are best practices to maintain RAID reliability.

















Ang PH Ranking ay nag-aalok ng pinakamataas na kalidad ng mga serbisyo sa website traffic sa Pilipinas. Nagbibigay kami ng iba’t ibang uri ng serbisyo sa trapiko para sa aming mga kliyente, kabilang ang website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, at TikTok traffic. Ang aming website ay may 100% kasiyahan ng customer, kaya maaari kang bumili ng malaking dami ng SEO traffic online nang may kumpiyansa. Sa halagang 720 PHP bawat buwan, maaari mong agad pataasin ang trapiko sa website, pagandahin ang SEO performance, at pataasin ang iyong mga benta!
Nahihirapan bang pumili ng traffic package? Makipag-ugnayan sa amin, at tutulungan ka ng aming staff.
Libreng Konsultasyon